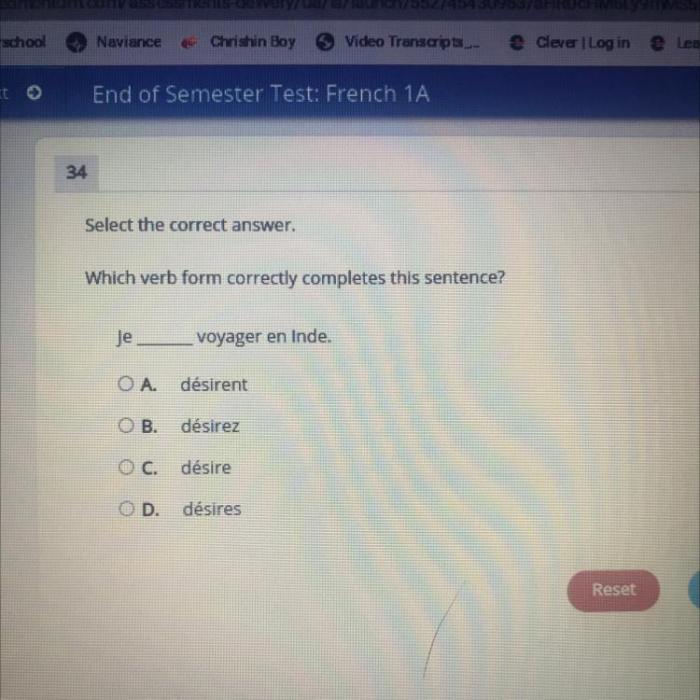
Which verb form correctly completes this sentence – Delving into the intricacies of English grammar, this comprehensive guide explores the fundamental concept of verb forms, empowering you to navigate the complexities of subject-verb agreement, tense, mood, voice, and conditional sentences. By mastering these essential building blocks, you will unlock the secrets of effective communication, ensuring that your words convey your intended meaning with precision and clarity.
Embark on this linguistic journey to unravel the mysteries of verb forms and elevate your writing to new heights of eloquence and sophistication.
Verb Forms
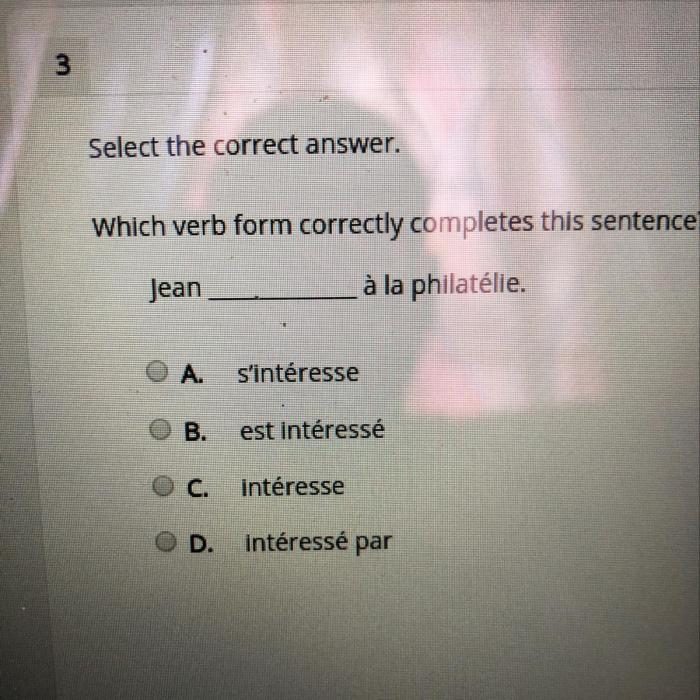
Verbs are words that describe actions, states, or occurrences. They can be classified into different forms based on their tense, aspect, mood, and voice. The following are the main verb forms in English grammar:
- Base form (also known as the infinitive form): to walk, to talk, to read
- Present tense: walks, talks, reads
- Past tense: walked, talked, read
- Future tense: will walk, will talk, will read
- Present perfect tense: has walked, has talked, has read
- Past perfect tense: had walked, had talked, had read
li>Future perfect tense: will have walked, will have talked, will have read
The choice of verb form depends on the time frame of the action or event being described, as well as the speaker’s perspective and purpose.
Subject-Verb Agreement
Subject-verb agreement refers to the grammatical rule that requires the verb in a sentence to match the number and person of its subject. In other words, a singular subject takes a singular verb, and a plural subject takes a plural verb.
- Example: The boy walks to school. (singular subject, singular verb)
- Example: The girls walk to school. (plural subject, plural verb)
There are some exceptions to this rule, such as when the subject is a collective noun or when the verb is in the passive voice.
Tense
Tense refers to the time frame of an action or event. English grammar has three main tenses:
- Present tense: describes actions or events that are happening now or are habitual.
- Past tense: describes actions or events that happened in the past.
- Future tense: describes actions or events that will happen in the future.
Each tense has its own set of rules for verb formation and usage.
Mood
Mood refers to the speaker’s attitude towards the action or event being described. There are three main moods in English grammar:
- Indicative mood: expresses facts or statements.
- Imperative mood: expresses commands or requests.
- Subjunctive mood: expresses wishes, possibilities, or hypothetical situations.
The choice of mood depends on the speaker’s purpose and the context of the sentence.
Voice
Voice refers to the relationship between the subject of a sentence and the action or event being described. There are two main voices in English grammar:
- Active voice: the subject of the sentence performs the action.
- Passive voice: the subject of the sentence receives the action.
The choice of voice depends on the emphasis the speaker wants to place on the subject or the action.
Conditional Sentences, Which verb form correctly completes this sentence
Conditional sentences express hypothetical situations or relationships between events. There are three main types of conditional sentences:
- Type 1: expresses a possible or probable condition.
- Type 2: expresses an unlikely or improbable condition.
- Type 3: expresses an impossible or hypothetical condition.
Each type of conditional sentence has its own set of rules for verb formation and usage.
Reported Speech
Reported speech is used to convey what someone said or wrote in the past. There are two main ways to report speech:
- Direct speech: the speaker’s words are quoted directly.
- Indirect speech: the speaker’s words are reported in the third person.
The choice of reporting method depends on the context and the speaker’s purpose.
Direct and Indirect Speech
Direct speech is the exact words spoken by a person, enclosed in quotation marks. Indirect speech reports what someone said without using quotation marks, and changes the pronouns, tenses, and sometimes the word order.
- Example: Direct speech: “I am going to the store,” she said.
- Example: Indirect speech: She said that she was going to the store.
The rules for converting direct speech to indirect speech and vice versa are complex and depend on the specific situation.
Active and Passive Voice
Active voice is used when the subject of a sentence performs the action. Passive voice is used when the subject of a sentence receives the action.
- Example: Active voice: The boy kicked the ball.
- Example: Passive voice: The ball was kicked by the boy.
The choice of voice depends on the emphasis the speaker wants to place on the subject or the action.
FAQ: Which Verb Form Correctly Completes This Sentence
What is the difference between a verb and a verb form?
A verb is a word that describes an action, occurrence, or state of being. A verb form is a specific variation of a verb that indicates its tense, mood, voice, or aspect.
How do I determine the correct verb form to use?
The correct verb form to use depends on the subject of the sentence, the time frame of the action or event, and the intended meaning.
What are the most common types of verb forms?
The most common types of verb forms include the present tense, past tense, future tense, present perfect tense, past perfect tense, and future perfect tense.