Biology corner transcription and translation – Welcome to the Biology Corner, where we embark on a captivating exploration of transcription and translation, fundamental processes in molecular biology. These intricate mechanisms orchestrate the flow of genetic information from DNA to RNA to protein, shaping the very fabric of life.
As we delve into the molecular intricacies of transcription and translation, we will unravel their profound implications in biotechnology, medicine, and our understanding of life itself.
1. Transcription and Translation Overview
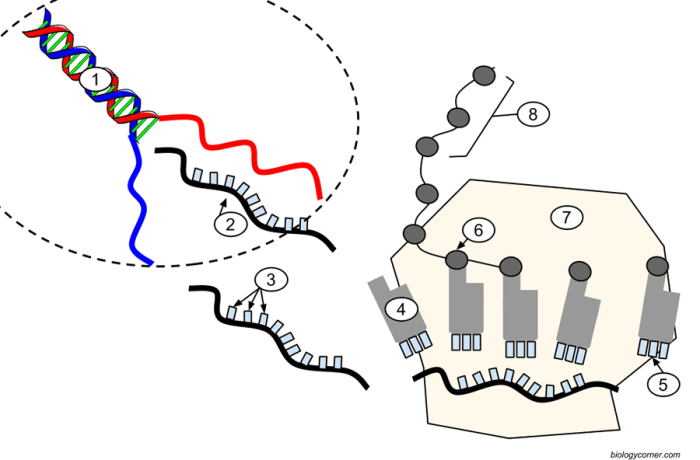
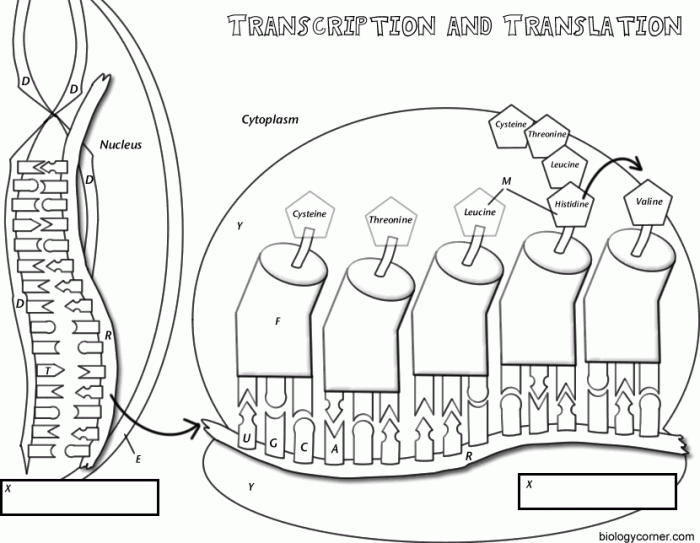
Transcription and translation are fundamental processes in molecular biology that allow cells to convert genetic information into functional proteins. Transcription involves the synthesis of RNA molecules from DNA templates, while translation involves the synthesis of proteins from RNA templates. Key players in these processes include RNA polymerase and ribosomes.
2. Transcription Process
Transcription occurs in three main steps: initiation, elongation, and termination. Initiation involves the binding of RNA polymerase to a specific DNA sequence called the promoter. Elongation involves the synthesis of an RNA molecule complementary to the DNA template strand. Termination involves the release of the RNA molecule and RNA polymerase from the DNA template.
Transcription regulation involves various mechanisms, including the role of promoters, transcription factors, and RNA polymerase. Promoters are specific DNA sequences that determine the initiation site of transcription. Transcription factors are proteins that bind to promoters and either promote or inhibit transcription.
3. Translation Process
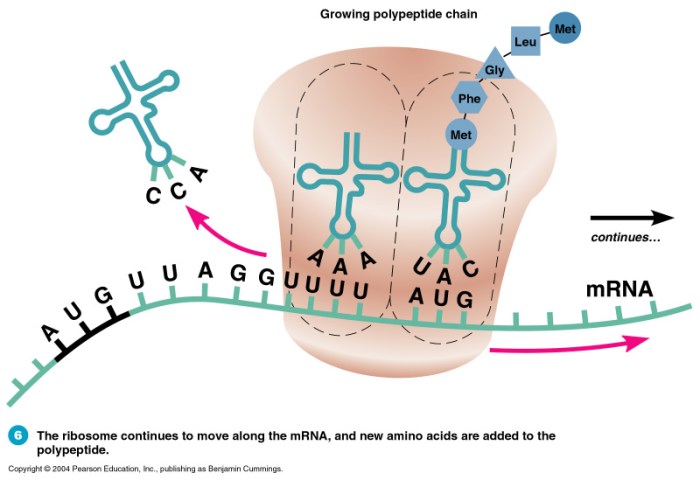
Translation occurs in three main steps: initiation, elongation, and termination. Initiation involves the binding of a ribosome to an mRNA molecule. Elongation involves the sequential addition of amino acids to the growing polypeptide chain. Termination involves the release of the polypeptide chain and ribosome from the mRNA molecule.
The ribosome, tRNA, and mRNA play crucial roles in protein synthesis. The ribosome is a complex structure that facilitates the translation process. tRNA molecules carry specific amino acids and bind to complementary codons on the mRNA molecule. The genetic code specifies the sequence of amino acids in proteins, and it is read during translation by the ribosome.
4. Regulation of Transcription and Translation
Transcription and translation are tightly regulated to ensure proper gene expression. Transcription factors, RNA stability, and microRNAs are involved in regulating gene expression. Transcription factors can activate or repress transcription by binding to specific DNA sequences. RNA stability influences the lifespan of mRNA molecules, affecting the amount of protein produced.
MicroRNAs are small RNA molecules that can bind to mRNA molecules and prevent their translation.
5. Errors in Transcription and Translation, Biology corner transcription and translation
Errors in transcription and translation can lead to the production of non-functional proteins. Transcription errors can occur due to DNA damage or errors in RNA polymerase. Translation errors can occur due to misreading of the genetic code or errors in tRNA binding.
These errors can have serious consequences for cell function.
Error correction mechanisms exist to minimize the impact of errors in transcription and translation. These mechanisms include proofreading by RNA polymerase and ribosomes, as well as post-translational modifications that can correct errors in protein folding.
6. Applications of Transcription and Translation
Transcription and translation are essential processes in biotechnology and medicine. They are used in gene therapy, drug development, and genetic engineering. Gene therapy involves introducing genetic material into cells to treat genetic disorders. Drug development involves using transcription and translation to produce therapeutic proteins.
Genetic engineering involves modifying the genetic material of organisms to improve their traits.
FAQs: Biology Corner Transcription And Translation
What is the key difference between transcription and translation?
Transcription converts DNA into RNA, while translation converts RNA into protein.
What is the role of RNA polymerase in transcription?
RNA polymerase binds to DNA and synthesizes a complementary RNA molecule.
How does the ribosome participate in translation?
The ribosome reads the mRNA sequence and assembles the corresponding amino acids into a polypeptide chain.
What are the potential consequences of errors in transcription or translation?
Errors can lead to non-functional or misfolded proteins, which can disrupt cellular processes.