The Potential Energy Kinetic Energy Worksheet serves as a comprehensive guide to understanding the fundamental concepts of potential and kinetic energy, their interrelationship, and their applications in real-world scenarios. This meticulously crafted worksheet provides an engaging and interactive learning experience, fostering a deeper comprehension of these critical energy forms.
This worksheet delves into the core principles of potential and kinetic energy, providing clear explanations and illustrative examples. It explores the conversion and conservation of energy, highlighting the role of friction and other factors in these processes. Additionally, the worksheet covers advanced concepts such as potential energy diagrams and kinetic energy distributions, demonstrating their significance in research and development.
Potential Energy and Kinetic Energy Concepts
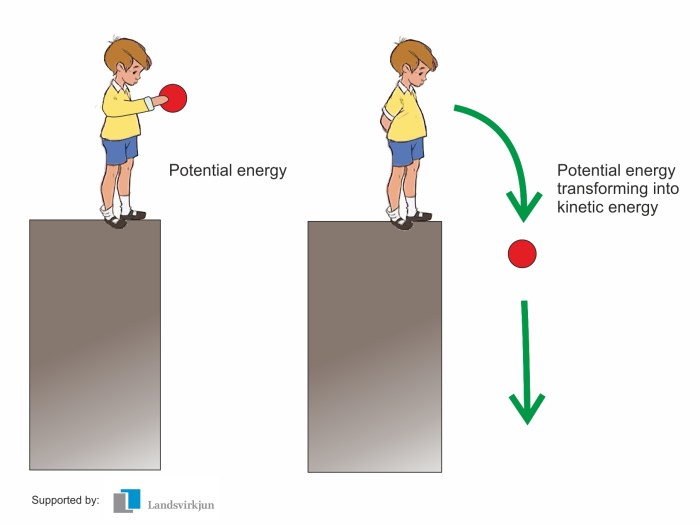
Energy exists in various forms, and potential energy and kinetic energy are two fundamental types. Potential energy refers to the energy an object possesses due to its position or condition, while kinetic energy is the energy of motion.
Potential Energy
Potential energy arises from an object’s position or state. It exists in two primary forms: gravitational potential energy and elastic potential energy. Gravitational potential energy is associated with an object’s height or position relative to a gravitational field, while elastic potential energy is stored in deformed objects, such as stretched springs or compressed gases.
Kinetic Energy
Kinetic energy is the energy of motion. It is directly proportional to an object’s mass and the square of its velocity. Kinetic energy increases as an object’s mass or velocity increases.
Relationship between Potential Energy and Kinetic Energy
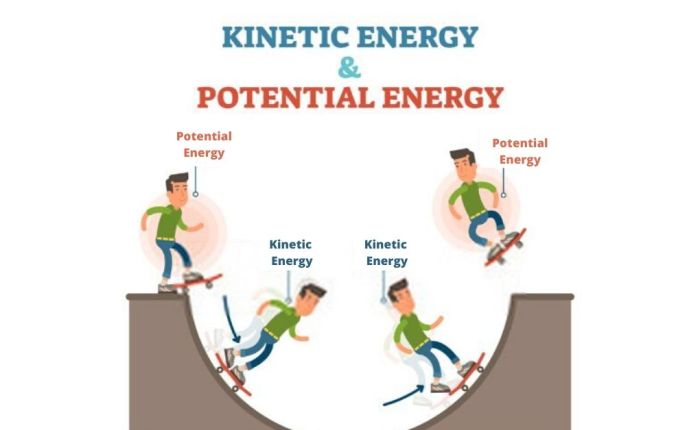
Potential energy can be converted into kinetic energy and vice versa. This conversion is often observed in mechanical systems. For instance, when an object falls due to gravity, its potential energy is transformed into kinetic energy as it gains speed.
Potential Energy Kinetic Energy Worksheet
A potential energy and kinetic energy worksheet provides practice problems and exercises to enhance understanding of these concepts.
Purpose of the Worksheet
The worksheet aims to:
- Reinforce the concepts of potential and kinetic energy.
- Develop problem-solving skills in applying these concepts.
- Foster critical thinking and analysis of real-world scenarios.
Applications of Potential Energy and Kinetic Energy
Potential energy and kinetic energy have numerous applications in various fields:
Engineering
- Design of structures and machines to withstand forces and optimize energy efficiency.
- Analysis of energy conversion in mechanical systems, such as engines and turbines.
Physics
- Understanding the motion of objects in gravitational fields, including projectiles and satellites.
- Exploration of energy conservation and conversion principles in various physical phenomena.
Sports and Recreation
- Analysis of energy transfer in sports activities, such as running, jumping, and cycling.
- Design of equipment and facilities to enhance performance and safety.
Energy Conversion and Conservation
Energy conversion refers to the transformation of energy from one form to another. Potential energy and kinetic energy can be interconverted through mechanical processes.
Principle of Energy Conservation
The principle of energy conservation states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only converted from one form to another. In mechanical systems, the total mechanical energy (potential energy + kinetic energy) remains constant in the absence of friction and other dissipative forces.
Potential Energy Kinetic Energy Calculations
Potential Energy Formula
Gravitational potential energy (PE): PE = mgh, where m is the mass, g is the acceleration due to gravity, and h is the height.
Elastic potential energy (PE): PE = 1/2kx 2, where k is the spring constant and x is the displacement.
Kinetic Energy Formula
Kinetic energy (KE): KE = 1/2mv 2, where m is the mass and v is the velocity.
Advanced Concepts in Potential Energy and Kinetic Energy
Potential Energy Diagrams
Potential energy diagrams graphically represent the variation of potential energy with position or displacement. They provide insights into the stability and equilibrium of systems.
Kinetic Energy Distributions
Kinetic energy distributions describe the spread of kinetic energy among particles in a system. They are crucial in statistical mechanics and quantum mechanics.
Limitations of Potential Energy and Kinetic Energy Concepts
While potential energy and kinetic energy are fundamental concepts, they have limitations in certain situations:
- Relativistic effects become significant at very high speeds, requiring relativistic energy equations.
- Quantum mechanics introduces wave-particle duality, where particles can exhibit both particle-like and wave-like properties, affecting the classical definitions of potential and kinetic energy.
Essential FAQs: Potential Energy Kinetic Energy Worksheet
What is potential energy?
Potential energy is the energy stored within an object due to its position or state. It can be gravitational, elastic, or chemical.
How is kinetic energy different from potential energy?
Kinetic energy is the energy of motion, while potential energy is stored energy. Kinetic energy depends on an object’s mass and velocity, while potential energy depends on its position or state.
What is the relationship between potential and kinetic energy?
Potential energy can be converted into kinetic energy, and vice versa. This conversion is often observed in real-world scenarios, such as a roller coaster or a pendulum.